CSS Position
The CSS position property is utilized to define an element's location on a web page.
The position property has five values as follows:
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
Static Position
This is the normal behavior. Elements are placed as per the standard flow of the page.
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE
html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS Position
</title>
</head>
<body>
<div
class="static">I am a box</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS
.static
{
position: static;
background-color: yellow;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
}
Output

Relative Position
Relative positioning positions an element in relation to its original position.
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE
html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS Position
</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="relative">I am a box</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS
.relative
{
position: relative;
top: 60px;
left: 90px;
background-color: yellow;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
}
Output

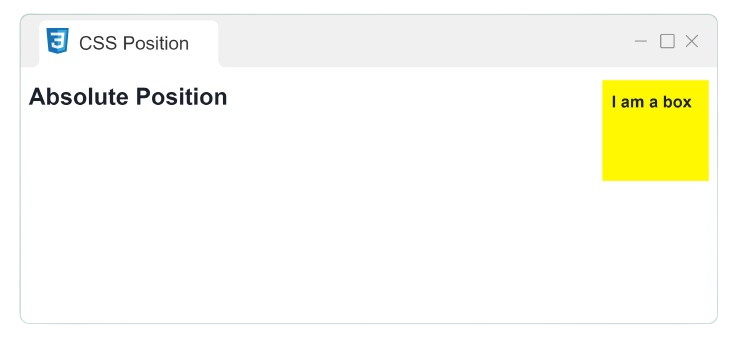
Absolute Position
The absolute value takes the element out of its regular flow in the document.
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE
html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS Position
</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="absolute">I am a box</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS
.absolute
{
position: absolute;
top: 60px;
left: 90px;
background-color: yellow;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
}
Output
Fixed Position
The fixed value holds an element in place so that it will not move its position even when the page is scrolled.
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE
html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS Position
</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="fixed">This paragraph has a fixed position.</div>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS
.fixed
{
position: fixed;
top: 60px;
background-color: yellow;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
}
p
{
border: 1px solid black;
}
Output

