CSS Z-index
The z-index property specifies an element's stacking order.
Example:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE
html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
CSS Z-index
</title>
</head>
<body>
<div
class="container">
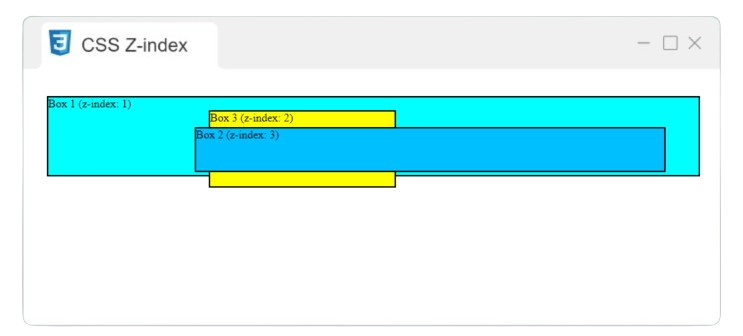
<div class="box1"> Box 1 (z-index: 1) </div>
<div class="box2"> Box 2 (z-index: 3) </div>
<div class="box3"> Box 3 (z-index: 2) </div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS
.container
{
position: relative;
}
.box1
{
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
border: 2px solid black;
height: 110px;
margin: 40px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.box2
{
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
background-color: deepskyblue;
height: 60px;
width: 66%;
left: 250px;
top: 44px;
border: 2px solid;
}
.box3
{
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
background-color: gray;
width: 26%;
left: 270px;
top: 20px;
height: 106px;
border: 2px solid;
}
Output